Investing Intelligently in Marketing Technology
A question that I often get asked is “What should I be investing in my Marketing Technology?”
Well, lets start with a definition of what Marketing Technology (aka MarTech) is:
“The suite of software and systems that a company directly owns and controls to manage, execute, and optimize its marketing operations—distinct from external platforms like AdTech used for paid media or advertising.”
This would typically be its website (Content Management System), Commerce, Product Information Management (PIM), Digital Assets Management (DAM), Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and order and stock management systems (Enterprise resource planning, ERP). From a costing perspective it also includes cloud hosting costs for those services and any costs associated with external agencies that help build or run the services.
It does not include things like spend on external marketing or advertising. It also does not include internal IT services such as running company hardware, laptops or servers or the HR systems (i.e. its not your overall IT spend)
A good benchmark for investment in any system is the proportion that it represents of your turnover. Clearly companies that are ‘natively digital’ are going to spend more proportionately than those that produce physical goods. Also, it seems that companies with a larger turnover spend proportionately more. What is clear though is that for any company, in any sector there is a ‘range’ or percentage that can be used as a benchmark.
This brief report outlines these MarTech spending benchmarks, but also looks at what can happen if you grossly overspend or grossly underspend against these benchmarks. And finally, I’ll give some indicators of how to manage projects and budgets so that you can remain on-track.
MarTech Spend According to Company Size
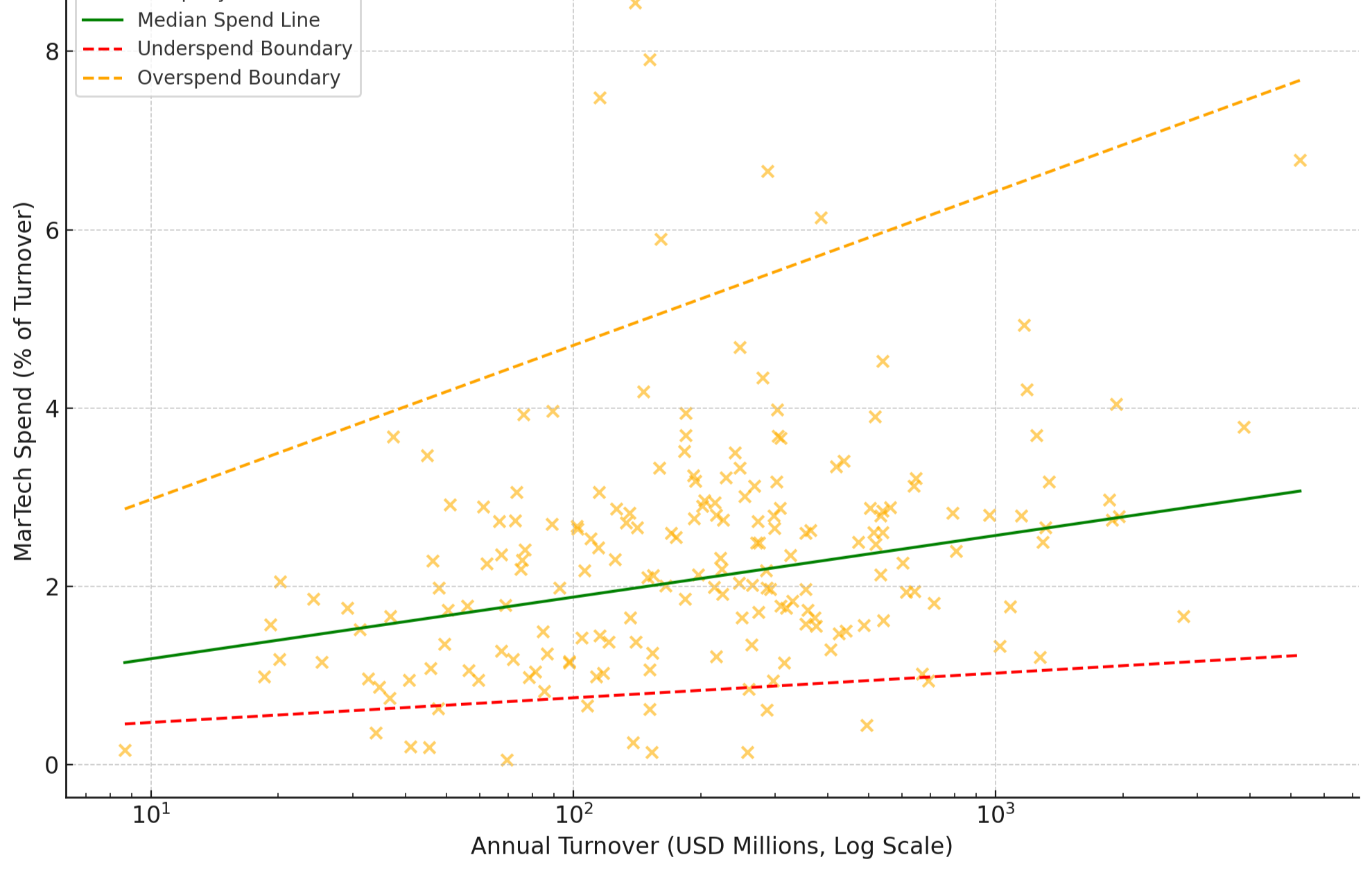
There is no ‘magic number’ when it comes to what a company should invest in the Marketing Stack, but if you look across different company sizes and different sectors a pattern emerges. The diagram below looks at 200 companies of different sizes and compares the proportion of their MarTech spend to Turnover against the overall turnover.
MarTech spend as a proportion (%) of turnover against Turnover (USD millions)
Very roughly one can say that larger companies invest proportionally more in MarTech, but as a rough rule companies typically allocate between 1% to 5% of their annual revenue to MarTech.
Small Businesses (<$50M Revenue): 0.5%–2% of revenue, or £50K–£500K annually.
Mid-Market ($50M–$500M Revenue): 1%–3% of revenue, or £500K–£5M annually.
Enterprise (>$500M Revenue): 2%–4% of revenue, scaling from £10M to £100M+.
Going into a little more detail, but still very generally; Of the total MarTech expenditure, the major categories are as follows:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: 25%
Content Management Systems (CMS) & Commerce: 20%
Enterprise resource Planning (ERP) & Order Management: 25%
Product Information Management (PIM) & Digital Asset Management (DAM): 15%
Cloud Hosting & Integration (e.g. AWS, Kubernetes, Azure): 15%
Again, of course these numbers are indicative, not definitive. Service or software companies might not run a PIM and there are multiple other MarTech systems that aren’t exactly accounted for in this list and some (like Order Management) that are simply rolled into Commerce or ERP.
As an example though, if you’re turning over £100M, you should roughly be spending 2%, or £2M annually on your MarTech. Of that, you might commit 20% or £400,000 to your Website (CMS/DXP) and Commerce. This may seem high, but these are annualised Cost of Ownership (CoS) so this would be the cost of a build program evened out over the period of ownership.
MarTech spend in different sectors
Different sectors with a different focus will clearly vary greatly in their spend commitments. Not surprisingly Retail and Commerce are going to be at the high end - sometimes up to 15% of their turnover - as they have clearly understood the value of the digital channel. At the other end of the spectrum, companies in Manufacturing (and even more so in Engineering) might be on the lower end of the spectrum
Spend, as a percentage of revenue, is influenced by factors such as digital maturity, customer engagement needs, and competitive pressures. While specific data for all sectors is limited, general trends indicate the following:
Retail and E-commerce: Typically allocate a higher percentage of revenue to MarTech to enhance customer experiences and drive online sales.
Financial Services: Invest substantially in MarTech for personalized marketing and customer relationship management, balancing innovation with regulatory compliance.
Healthcare: Historically, MarTech spending has been lower due to stringent regulations, though investment is increasing to improve patient engagement and telemedicine services.
Manufacturing: Generally allocate less to MarTech, focusing more on operational technologies, but are gradually adopting digital marketing tools to support B2B sales.
For a more precise understanding of MarTech spending within a specific sector, consulting industry-specific reports or market research studies would provide the most accurate insights.
The Challenge of Getting MarTech Spend Right
While investment in MarTech is essential for growth, agility, and competitiveness, determining the appropriate level of spend is notoriously difficult. Many companies either over-spend on complex, overlapping systems or under-spend and fall behind digitally.
The cost of digital transformation needs to be right for your organisation. High investment shows commitment to the digital channels, but over-over-spending is reckless and dangerous for the organisation. Equally cautious underspending may be required to maintain profitability, but under-under-spending is also a route to failure.
Look at the outliers above and below the dotted lines on the scatter diagram - these are companies in the danger zone.
Why Do Companies Overspend?
Systems integrators and Digital agencies will perhaps laugh out loud when they hear 7- or 8-figure build costs presented to usually-governmental organisations from usually-big-6 consultants for digital transformations. Comments are usually along the lines of “We could have done that for half-the-price” but actually what is often implied is “I wish we’d taken them for that ride!” There is a tendency for big organisations to feel that they need to pay large licenses for software and pay high costs for consultants so they get a service that ‘matches’ their business. Unfortunately too many vendors and agencies will set their price tag, not according to a rate card, but according to your turnover.
Overspending on MarTech is a common challenge due to several factors:
Redundant Tools: Buying multiple platforms with overlapping functions. If you don’t understand the feature functionality of the platform you are purchasing, or aren’t leveraging the platform for all its capabilities, chances are you’ve got multiple systems doing the same thing.
Low Utilization: Underused subscriptions and poorly adopted systems. All of the platforms in the portfolio need to be cost audited - do we still need all these licenses?
Poor Integration: Extra costs from trying to connect disparate tools. It's one thing to struggle to connect legacy or proprietary systems, but if you’re building greenfield and your systems don’t work together, then somebody is making poor decisions.
Reactive Buying: Tech purchases made in response to short-term pressure. This can also result of a lack of joined up processes in procurement or across departments.
Lack of Strategy: Absence of a clear roadmap linked to business goals. There is classically a gap between business strategy and technical strategy (Marketing not talking to IT).
Vendor Lock-In: Staying with suboptimal platforms due to sunk costs. Technology moves so fast now, 5 year contracts are redundant, even 3 years is excessive. Lock in the best price for the shortest period and remain agile.
Hidden Costs: Underestimating total cost of ownership (TCO), including training, support, and customization. High TCO goes hand in hand with unnecessary complexity.
While technical selection does not have to be a long drawn out process with 100-page RFPs it does need to be part of a considered and well-thought-out overall business strategy. Some companies make the mistake of technology first, and then they painfully try and fit everything else in their organisation around the technology. Equally for others the technology is the least well-considered aspect and very poor decisions are made.
The important thing is not to buy the stuff that your mate on the golf course recommended - get a consultant who knows both Marketing and Technology. There are over 14,000 MarTech systems out there, so nobody knows them all, but a good consultant will have the experience to understand your business and recommend systems that work well in combination.
Why Do Companies Underspend and What are the Consequences?
While some firms over-spend, others significantly under-spend on MarTech — and the consequences can be just as damaging. Being a bit ‘tight on cash’ is rarely the main reason for under-spend it can be other factors or a combination of:
Budget Misallocation: Prioritizing other spend over core tech. For example if you redirect spending towards Advertising to drive more traffic, if your MarTech can’t handle it and falls over, the money is misspent.
Lack of Digital Maturity: Leadership underestimating tech's strategic value. This is very common in non-digital environments; manufacturing, logistics and even healthcare.
Change Aversion: Fear of complex rollouts or team disruption. Most digital Transformation is proven to improve team happiness and helps retain staff longer, so the fear should be of doing nothing
Manual Comfort Zones: Teams clinging to spreadsheets and legacy tools. Sales people running around with ‘little black books’, “this is how we’ve always done business”. Not a strategy that will keep you around for long.
52% of Fortune 500 companies that were on the list in 2000 have disappeared from the list since then. Adapt or die.
The benefits of going digital are too numerous to list but you can be absolutely certain that if you don’t invest, your competitors will be. It perhaps sounds like a cliche, but the cost of change is always quite high, but compare that to the cost of doing nothing?
How to Develop an Investment Program That Shows Value at Every Stage
So, having established roughly what spend your company should be looking at, the bigger question is always going to be how can you justify that spend? The answer is to build out a roadmap for continuously developing your MarTech stack, the processes around it and, most importantly, training the people to harness its power to the maximum
There is little appetite for ‘big bang’ builds that the stakeholders wait years for - its more important to deliver multiple-stage projects that deliver new value to the customer at every stage.
To get that process going, there are a few areas to look at immediately:
Align to Business Goals: Ensure tech investments map directly to strategic priorities. There is no business without Tech, and equally Tech is nothing without the business. These are not two silos, it's a symbiosis.
Audit Current Stack: Identify what's working, what’s overlapping, and what’s underused. How often have I seen 6-figure investments in ‘amazing’ Digital Experience Platforms (DXP) that are being used as glorified Content Management systems (CMS). Use it properly, or cut it out.
Define Future-State Architecture: Outline an ideal stack that scales. Set out the ‘North Star’. You won’t get there tomorrow, but you’ll always know your direction
Budget by Capability Clusters: Allocate budget across data, content, engagement, and commerce. While these areas shouldn’t be siloed, budgeting gives you a really go way of prioritising data. For example, should there be more in Client or Product?
Phased Rollouts: Use Agile and Stage-Gate frameworks for lower risk and better feedback. Find a framework that you’re comfortable with and make sure that each milestone, sprint, or stage is measurable in terms of value.
Cross-Functional Ownership: Involve Marketing, IT, Sales, and Finance. Siloed communication is a recipe for failure. Bridge the gaps - find people who have cross-functional capabilities and talk.
TCO & ROI Models: Justify every investment with value-based metrics. Measure everything. If you can’t measure it you have no yardstick for success or failure
Continuous Evaluation: Reassess tools and performance every quarter. This is not one and done. Continuously experiment, prototype and be merciless with what doesn’t work.
API-First Platforms: Favour modular systems for long-term flexibility. Don’t fall for the “one system does all” sales pitch. That's a monolith and will fail. Look for “Best of need” platforms that suit your business and budget
Project Governance: Use MoSCoW, RACI or Agile planning for control and clarity. Structure, planning, data, analytics are your tools to make sure progress is made. This is not ‘big bang’ or ‘one and done’ or ‘in and out’ this is a long game, know the rules.
References
Gartner CMO Spend Survey, 2023
Forrester: The State of Martech, 2024
MarTech Annual Stack Audit Report, 2023
IDC Worldwide Digital Transformation Spending Guide
CMSWire: Martech Stack Optimization Tips
Harvard Business Review: Why Digital Transformations Fail
Deloitte Insights: Digital Maturity Index